5G is changing the way we interact, communicate, and use information.
With speeds several times faster than 4G, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect billions of devices, 5G is powering everything from smart cities to self-driving vehicles.
But with those advancements come actual security dangers. With even more complex networks and more devices linking in real-time, the possibility of cyber attacks is much more substantial.

5G network security is no longer a technical afterthought. It’s a necessity for individuals, businesses, and entire infrastructures. Whether you’re a mobile user or a tech leader, understanding these risks and how to manage them is critical in 2025 and beyond.
In this guide, we will examine what 5G network security is. What are the biggest threats it presents to a connected world? What methods protect against them, and how do best practices guarantee that you’re protected?
- What is 5G Network Security?
- Threats to 5G Network Security
- Key Aspects of 5G Network Security
- Security Standards and Regulations for 5G Networks
- Improved Security Solutions for 5G Networks
- Best Practices for Securing 5G Networks
- Real-World Case Study-Huawei & UK 5G Ban
- The Future of 5G Network Security
- Final Thoughts on 5G Network Security and the Road Ahead
- FAQs
What is 5G Network Security?
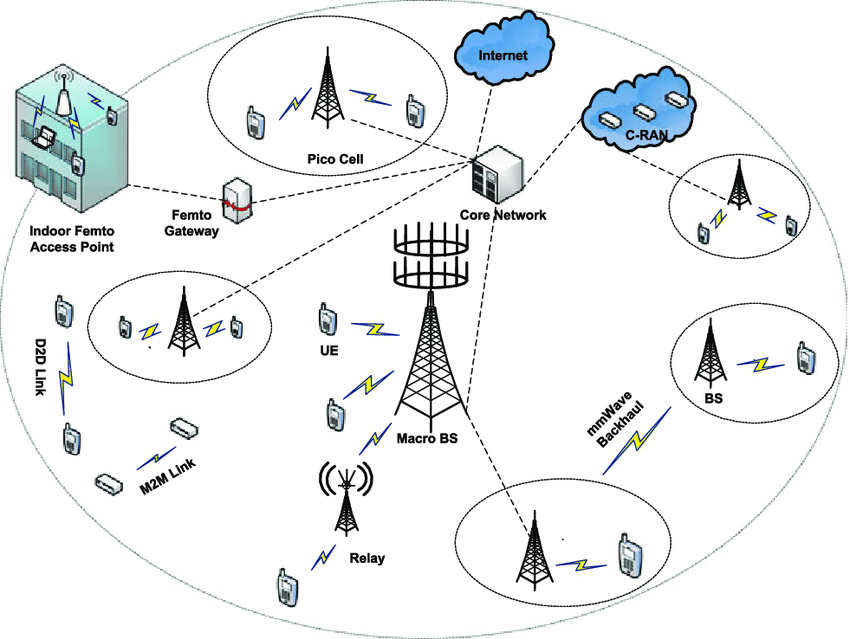
5G network security is techniques and technologies that are used to protect the data, devices, and hardware in 5G wireless networks.
It involves encryption, authentication, protection from network slicing, and threat detection in real-time.
5G networks support mission-critical services like healthcare, finance, transportation, and smart homes.
A 5G security attack can cause massive data breaches, infrastructure freezing, or timely monitoring of users.
As opposed to other generations, 5G is open and decentralized and thus it’s more agile, yet exposed.
What 5G Security Must Protect
- End-user devices (phones, wearables, IoT devices)
- Core and edge network infrastructure.
- Data-in-motion between cloud platforms and base stations.
- Industry or service-specific network slices.
Also Read: How to Conduct a Network Security Audit: Step-by-Step Guide
Threats to 5G Network Security
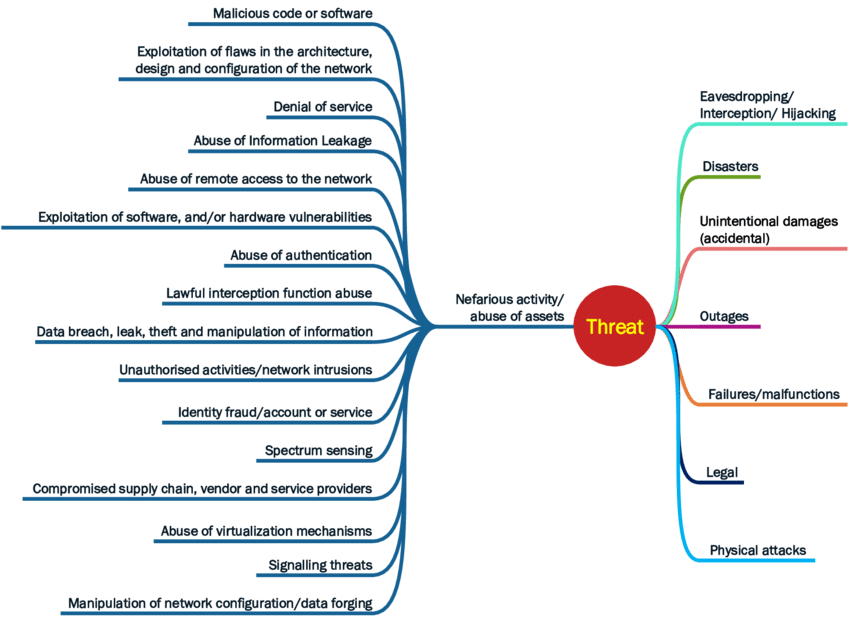
1. Hacking and Cyber Attacks
- 5G infrastructure can be targeted by hackers or state actors.
- Third-party vendor reliance and decentralized networks make it simpler for networks to be compromised.
- Disruption of essential services like power or transport is feasible.
2. Data breaches
- 5G contains high-volume, high-speed data transfer, so this is a natural target.
- Hackers can make use of weak encryption or insecure endpoints to collect sensitive data from people or organizations.
- Most exposed to industries handling real-time data, including healthcare and finance.
3. Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS Attacks
- Attackers can flood the network with fictitious traffic to bring servers or base stations down.
- This can shut services, apps, or even network slices temporarily down.
4. Privacy Violations
- 5G enables precise geolocation, face recognition, and live tracking.
- Unless protected strongly, user privacy will be susceptible to hackers as well as illegal tracking.
- IoT devices especially are prone to leaking behavioral or personal information.
5. Spoofing 5G Apps, Fake Links & Phishing
- Users may download malware unknowingly or click on spoofed upgrade links.
- 5G’s speeds allow threats (like phishing websites) to load instantaneously, increasing risk.
- Common in SMS scams or impersonation provider messages.
Key Aspects of 5G Network Security
1. Network Slicing Security
- 5G networks can be divided into “slices” for different services.
- Each slice needs to have separate security policies to prevent cross-contamination of threats between them.
- Without security, a compromise in one slice could spread to others.
2. Authentication and Encryption
- Prohibits unauthorized devices and users from joining the network.
- End-to-end encryption ensures data protection while in transit, especially in IoT and mobile communication.
- Ensures identification of the user and integrity of the data.
3. Edge Computing Security
- 5G shifts processing of data to the edge for better performance.
- Provides new local attack surfaces (e.g., edge nodes or routers).
- Requires strong encryption, device authentication, and firewalling at the edge.
4. Zero Trust Architecture
- “Never trust, always verify” each device, user, and application must be verified at all times.
- No default trust, not even to internal systems.
- Reduces lateral movement in the case of a breach.
Security Standards and Regulations for 5G Networks
1. Global Security Frameworks
- 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project): Specifies the 5G global security standards like encryption, authentication, and privacy.
- ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union – Telecommunication): Provides security and policy rules internationally.
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): Offers widespread cyber security frameworks adopted by governments and organizations internationally.
2. Regulatory Compliance
- There are various standards and data protection acts in nations like the USA, EU, China, and UK.
- Example: The EU GDPR applies to data that is shared over 5G networks as well.
3. Security of Vendors and Equipment
- Governments will ban or restrict high-risk vendors (e.g., Huawei).
- Supply chain security centered on the aspect that routers, antennas, and switches are tamper-proof.
- Zero-trust policies are often applied to third-party devices.
4. Risk Management and Mitigation
Involves vulnerability scanning and preparing for cyber incidents.
Comprises:
- Penetration testing
- Security audits
- Incident response planning
- Recent updates and patching
Recommended Read: Top Risks in Cloud Network Security and How to Address Them
Improved Security Solutions for 5G Networks
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- AI provides real-time detection of anomalies and threats via sophisticated 5G landscapes.
- ML anticipates cyberattacks by recognizing patterns in network traffic.
- Enables automated response systems to close down threats at the click of a button before they spread.
2. Blockchain for Network Integrity
- Provides a decentralized, tamper-evident ledger to track devices and transactions.
- Assists in verifying devices and obtaining data trust in IoT-saturated 5G networks.
- Prevents spoofing, copying, and unauthorized access to devices.
3. Post-Quantum Cryptography (Quantum-Resistant Encryption)
- Protects Against Future Quantum Threats: Prepares 5G networks for the future, where quantum computers could break today’s encryption methods.
- Uses New Mathematical Algorithms: Post-quantum cryptography uses specially designed algorithms that are resistant to quantum-based attacks.
- Still Under Development: This technology is not yet widely used, but it is being actively researched around the world to secure future networks.
Best Practices for Securing 5G Networks
- Use end-to-end encryption to protect all data in transit and at rest.
- Implement a zero-trust security model to authenticate all users and devices.
- Segment the network to compartmentalize important functions and limit breach impact.
- Keep systems, software, and hardware updated.
- Audit and test third-party vendors for security compliance.
- Ongoing monitoring of network activity and a prepared incident response plan.
Real-World Case Study-Huawei & UK 5G Ban
Context: In 2020, the UK government issued a ban on Huawei equipment in its 5G networks based on concerns regarding national security.
Reason: Fears that Huawei’s ties to the Chinese government could lead to surveillance, data interception, or foreign interference.
Action Taken:
- Telecom operators were instructed to stop installing Huawei gear from September 2021.
- All current Huawei gear to be taken out by 2027.
- A new Telecom Security Bill was published to implement these steps.
Investment:
The UK announced a £250m diversification strategy to reduce reliance on a concentrated number of telecoms suppliers and build a more diversified, resilient and competitive supply chain.
Lesson Learned:
National 5G security is more than technical solutions and vendor trust.
Governments must consider geopolitical risk, not technical standards, when securing 5G infrastructure.
The Future of 5G Network Security
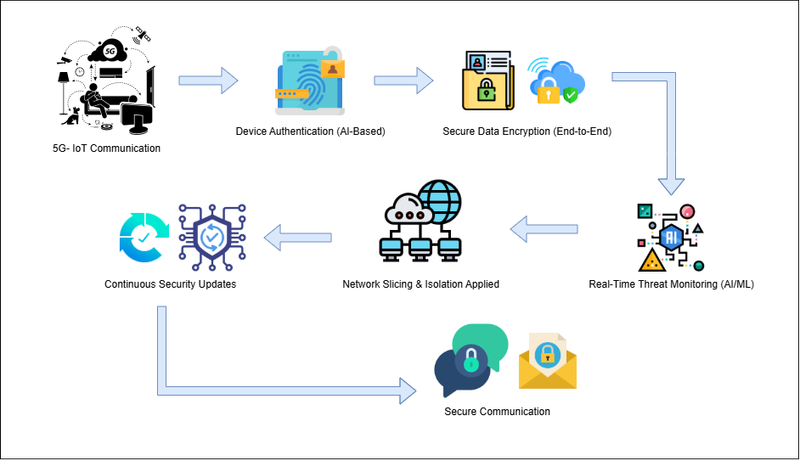
- AI-based attacks will rise; defenses must use real-time AI threat detection.
- Supply chain security will be critical; qualified vendors will be favored.
- Quantum-resistant encryption will be utilized to safeguard against future quantum attacks in advance.
- International security standards will get tighter, with more regulation and enforcement.
- End-user awareness will rise; end-users will be more responsible for data protection.
- Zero-trust architecture will be the standard for business and government networks.
Final Thoughts on 5G Network Security and the Road Ahead
Staying up to date, adopting best practices, and being aware of existing world threats, including vendor trust and Phishing attacks are crucial steps towards protection. As a mobile user or business manager, the time to get serious about 5G security is now.
The future of connectivity will be speedy but must also be secure.
Visit our Cyber-security page; we have the best guides for you. If you’re interested in contributing, submit your guest post and Write for Us.
FAQs
What is 5G network security?
5G network security refers to the tools, technologies, and strategies used to protect data, devices, and network infrastructure within 5G wireless systems. It includes encryption, authentication, network slicing protection, and real-time threat detection.
Why did the UK ban Huawei from its 5G network?
The UK banned Huawei in 2020 over national security concerns about the company’s ties to the Chinese government. The decision led to a phased removal of Huawei equipment and a £250 million investment in building a safer telecom supply chain.