Today, banking, healthcare, information, communications, and even the running of the government relies primarily on technology. With all such valuable data available on the internet, it is exponentially easier for cyber-attacks to be launched. Microsoft reports that over 600 million cyber-attacks occur every day worldwide, so cyber-security remains one of the most critical requirements of the times.
But what is cyber-security and why is it so important, and in which categories? This article explains Cyber-security in simple words, types of cyber-security, what are the general threats to the web world, and tips on how to be safe.
What is Cyber-Security?
Cyber-security, or IT security or information security, refers to the practice of securing systems, networks, devices, and data from cyber attacks. Cyber-security includes defense against unauthorized use, hacking, malicious software attack, phishing attacks, and other computer attacks. Cyber-security is no longer reserved for large corporations and the government, it’s something everyone needs, from employees and students to small businesses and global organizations.
Why Cyber-Security is Essential
Cyber-security concerns by its impactful benefits:
- Protection of Data: Barriers sensitive data like passwords, bank accounts, or medical information from being accessed.
- Protection of Money: Minimizes the risk of expensive breaches, ransomware payouts, and loss of business.
- Trust and Reputation: A company with good cyber security provides customer trust.
- National Security: Governments secure critical infrastructure like defense, energy, and communication systems from cyber war.
- Legal compliance: Organizations must be legally compliant with the Europe GDPR law, USA HIPAA, or Pakistan’s PECA 2016 in order to gain access to user information.
Types of Cyber-security
1. Network Security
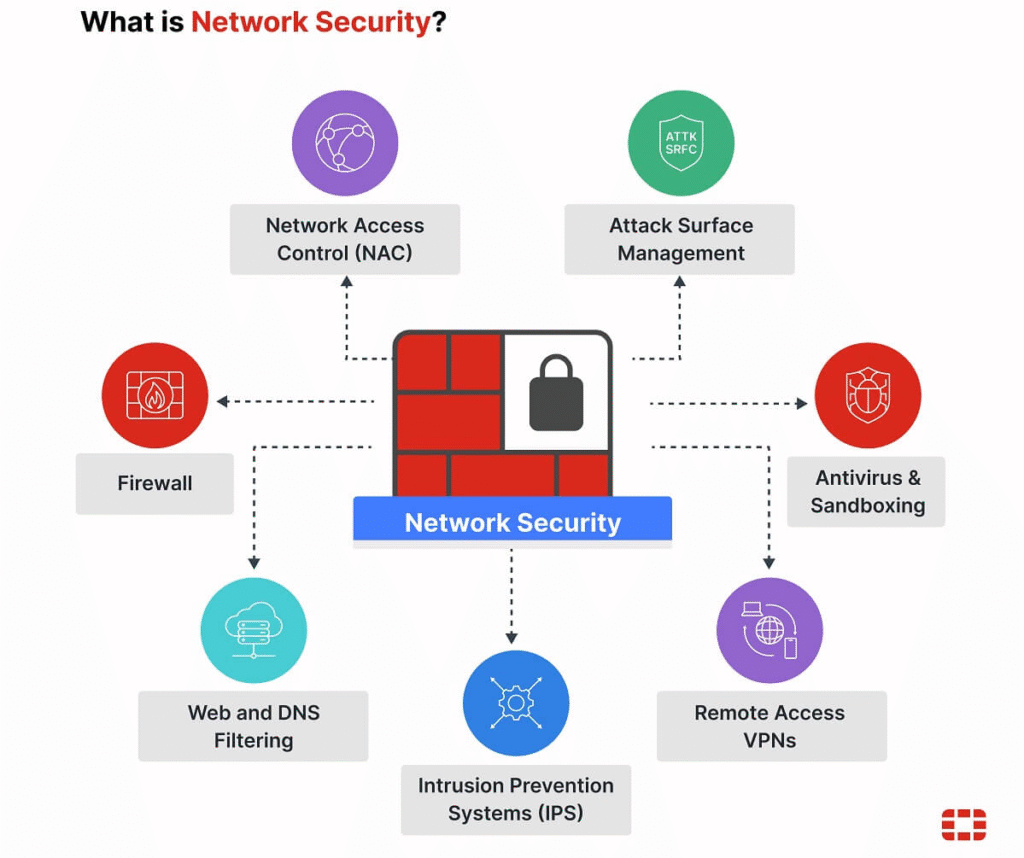
Network security protects internal systems by blocking unauthorized access through firewalls, VPN, and intrusion detection tools. Included among some of these devices are hardware and software firewall intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), network segmentation (so one breach will not expose all systems), VPNs, and next-generation firewalls with deep-packet inspection.
Solutions today move towards adaptive, AI-driven network defenses that acclimate to the real-time threat profiles. Dynamically retrainable firewalls are one such new concept, using machine learning platforms to record traffic adaptations.
2. Application Security
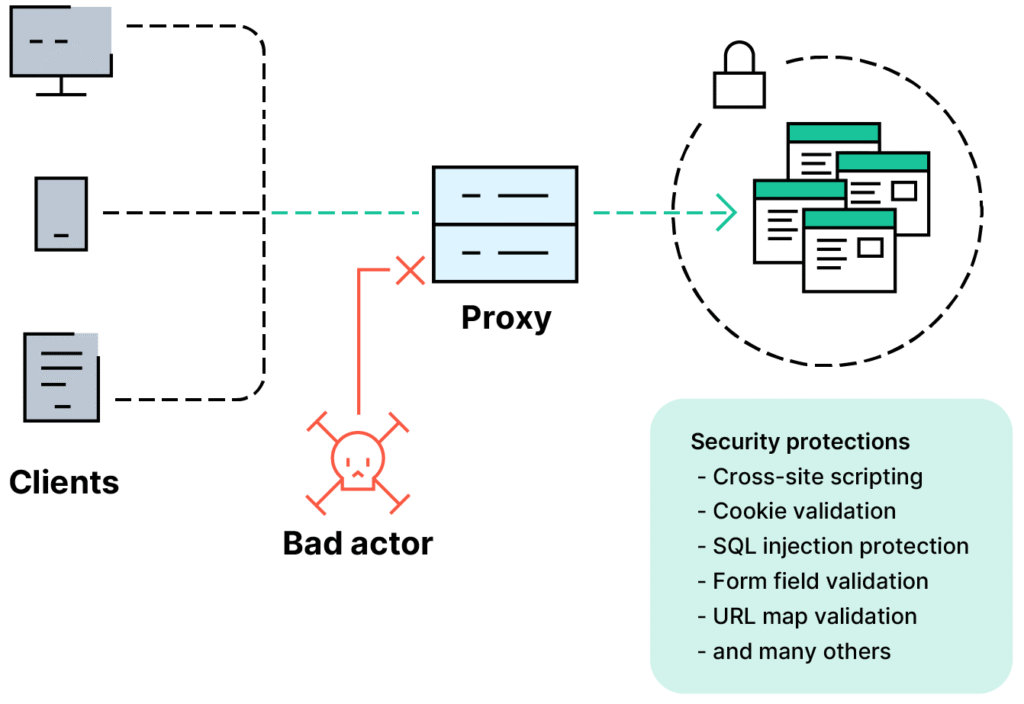
A vulnerability can be a vulnerable application. Application security attempts to create secure software from the start, by secure design, threat modeling, code review, static/dynamic analysis, runtime defenses, and patching. Web Application Firewalls(WAFs) offer protection from web-based attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), etc.
3. Information / Data Security
Even if systems are breached, secured or encrypted data remains secure. Access controls (who is able to view or modify data), encryption (AES, TLS, etc.), and masking or tokenizing of data safeguard sensitive information from release. Backup procedures, storage in order, and erase policies fall under this too.
4. Operational Security
This talks about how processes, policies, and workflows govern data handling and system access. This involves controlling policy, role-based access control, principle of least privilege, process auditing, and controlling policy (i.e. when data has to be released, deleted, moved, or archived). Human error is used mainly when attacking.
5. Cloud Security
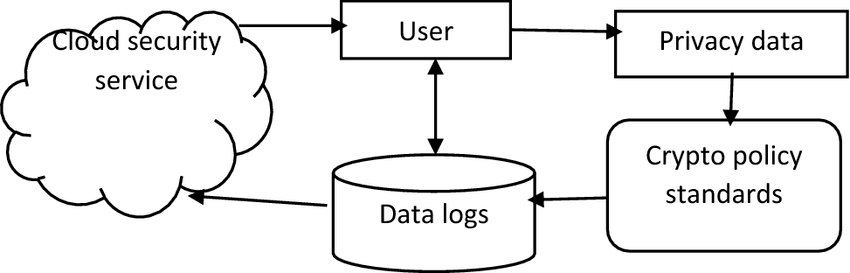
As companies move to the cloud, multi-cloud and hybrid deployments add risk vectors. Cloud security is safe configuration, identity & access management, monitoring, encryption, network segregation, and knowing the shared responsibility model (provider responsibility vs. customer responsibility). Public cloud security misconfiguration is a leading cause of breaches.
Read More: Cloud Security: Protecting Data, Apps, and Infrastructure
6. IoT / Embedded Device Security
With billions of networked wearables, industrial sensors, and smart homes, IoT security was a fresh threat. IoT security entails the practice of firmware update, device authentication, secure boot, anomaly detection, and network segmentation. IoT devices are more and more being used as a gateway into the larger systems that they are a component of.
7. Endpoint / Device Security
Endpoint (workstations, mobiles) remain the most targeted. Security agent tools for endpoints such as host-based firewalls, scheduled patching, disk encryption, antivirus, endpoint detection and response (EDR) safeguard the machines. Zero-day security and behavior monitoring are playing an increasingly significant role.
Read More: What is Endpoint Security? Definition, Importance & How It Works
8. Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity

There is no perfect system. A well-functioning cyber security system has worst-case thinking disaster, hardware failure, outages, or attacks. Failover support and restore, continuity of operations, and incident response planning enable companies to get back to work quickly and recover essential business processes.
9. Human / User Layer Security
Humans are the human factor. Phishing, re-use of credentials, insider attack, and social engineering all take advantage of human mistakes. Phishing simulations, policy adherence, education, password health, and proper multi-factor authentication (MFA) alleviate human risk.
10. Managed Detection & Response (MDR)
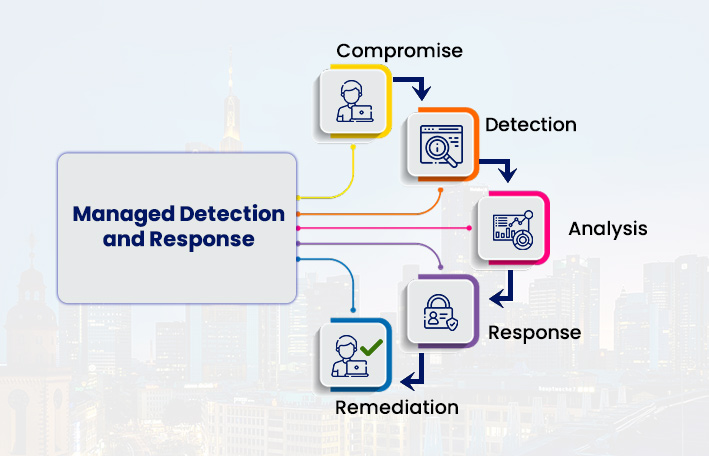
Few full-time security personnel are within most companies. MDR is a model of service in which security professionals watch around the clock, note, scan, and react to threats on behalf of the company, typically with visibility 24/7. This complements in-house capability.
Common Types of Cyber Threats
No good security if you do not know what you are defending against. Some of the most common cyber threats in 2025 are:
Malware
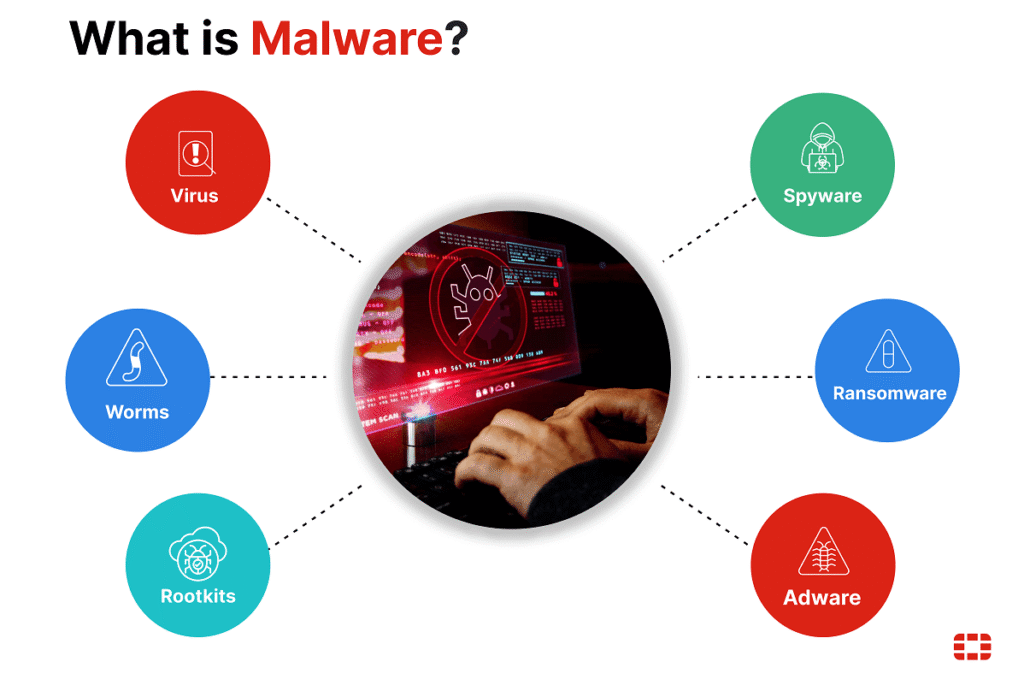
- The harmful software such as viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, ransomware, adware, and botnets.
- Ransomware is still a top threat:encrypts target files and demands payment for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks showed strong growth (e.g. 84% year-over-year growth in most regions).
- Botnets organize infected computers to carry out heinous attacks (e.g. DDoS).
- Spyware and keyloggers silently steal credentials or record activity.
Read More: How to Remove Malware From Mac Step by Step Guide
Phishing & Social Engineering
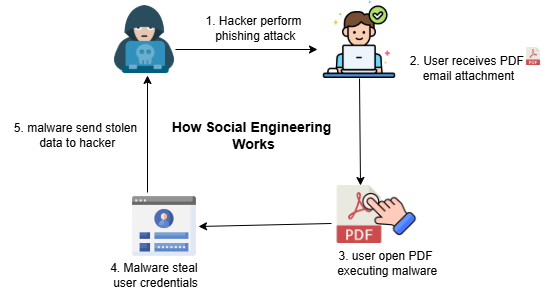
Threat actors develop emails, messages, or calls which deceive victims into handing over passwords, opening malware, or installing malware. Phishing attacks rose, particularly with legitimate-sounding content made through AI.
SQL Injection / Code Injection
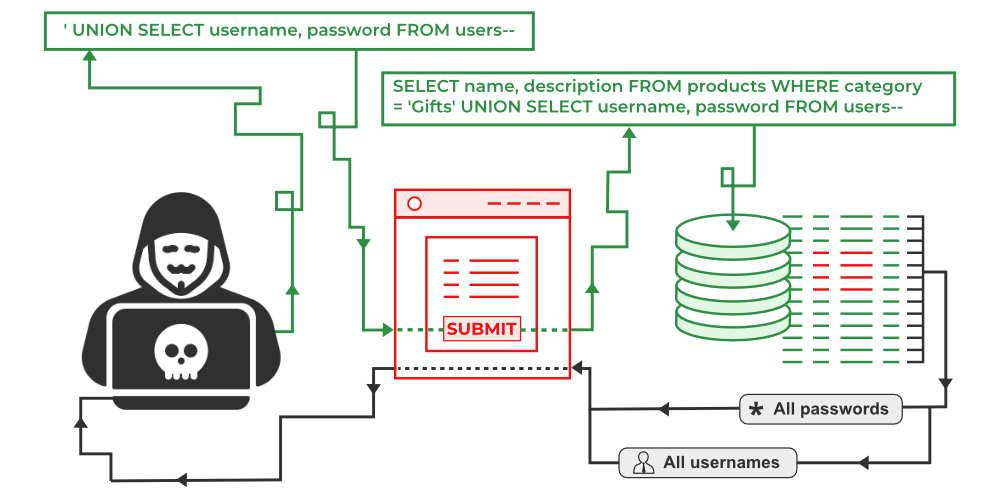
Malicious queries or code are injected by attackers into poorly sanitized input fields of web applications to obtain unauthorized database access or illicitly steal sensitive information.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM)
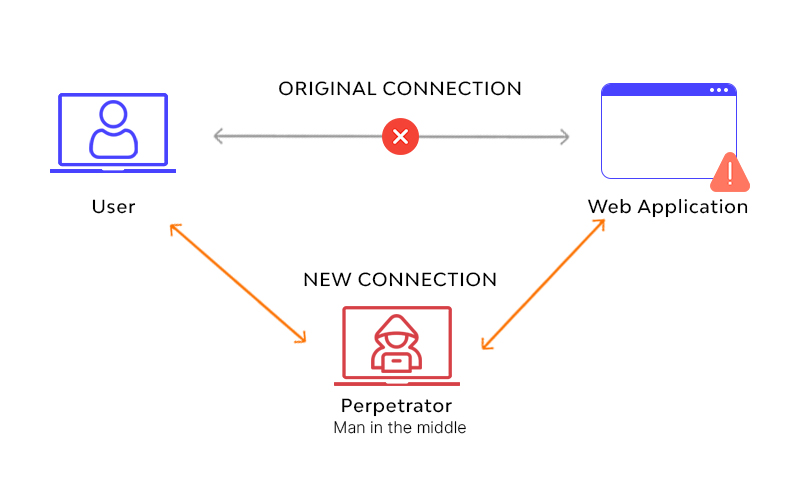
An attacker takes over a communication between parties (e.g. over insecure Wi-Fi) for intercepting or altering messages.
Denial-of-Service (DoS / DDoS)
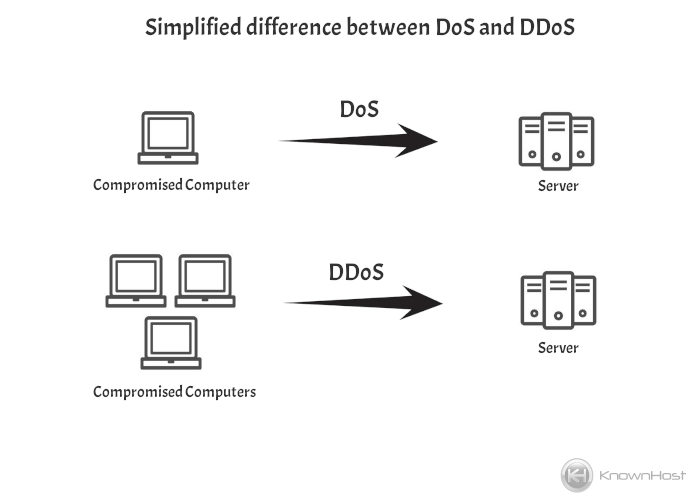
Sending incredibly high traffic to networks or servers in order to make them unavailable for service.
Zero-Day Exploits
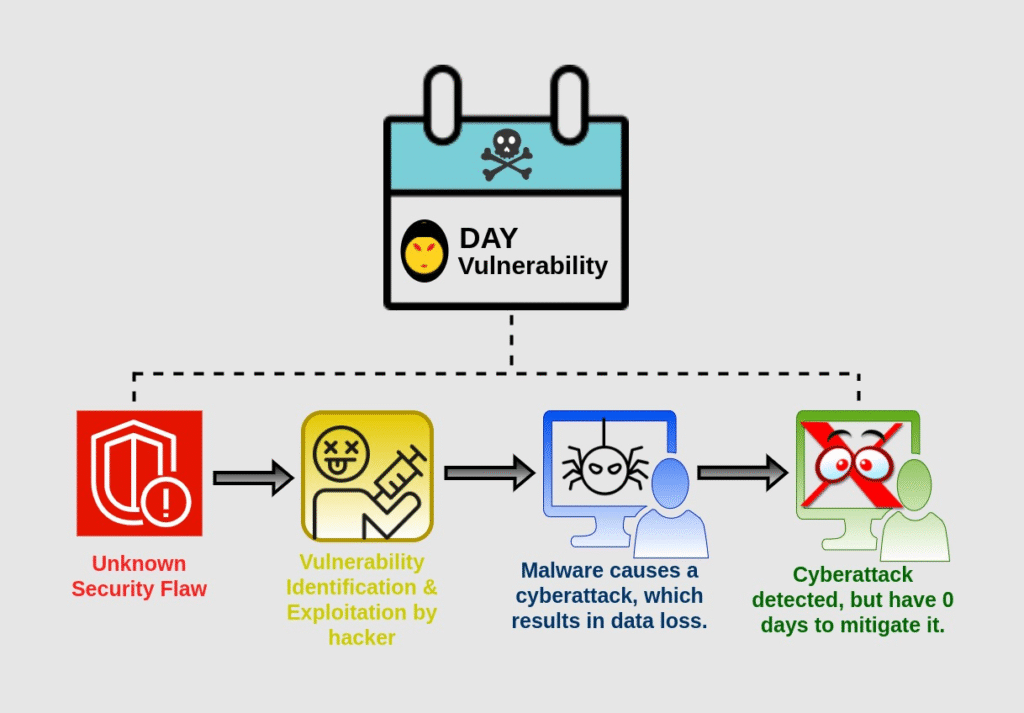
A secret to vendors prior to them even getting the opportunity to take advantage of it, leaving systems vulnerable until they are patched.
Insider Threats
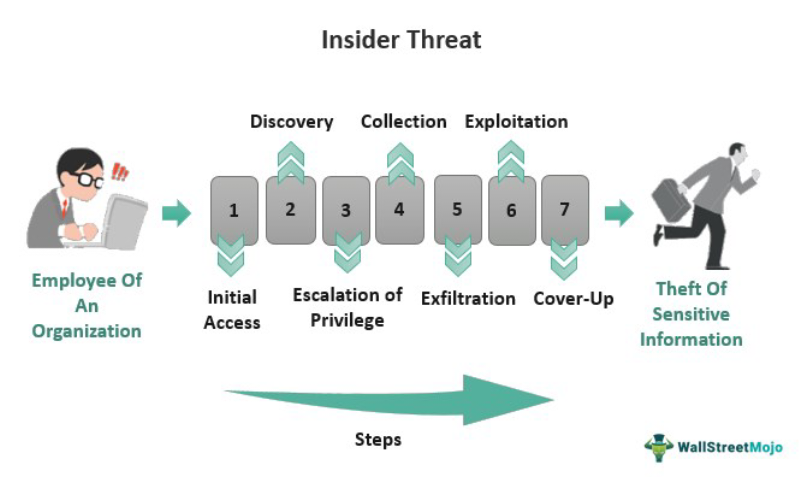
Legitimately authorized users (employees, contractors) misuse or leak information (accidentally or illegally).
Supply Chain Attacks
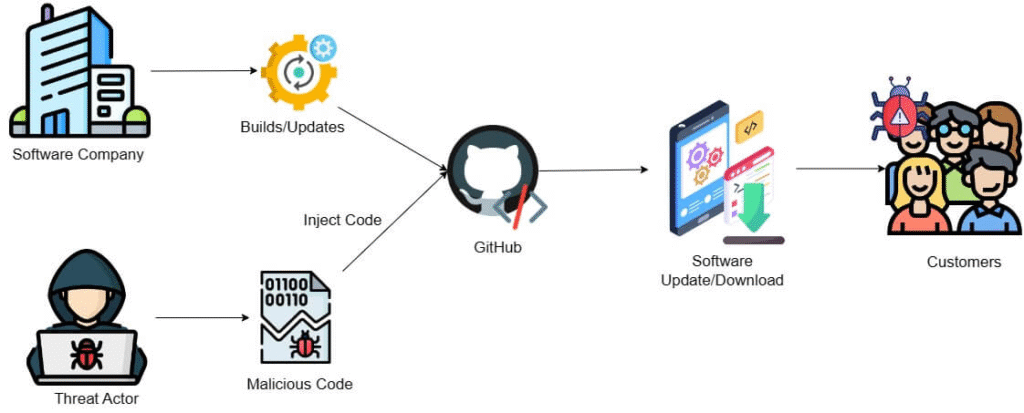
The attackers get control of software or hardware vendors and utilize them to introduce malware code or bugs, thereby impacting downstream customers.
Read More: How to Prevent Supply Chain Attacks
Credential Theft & Abuse
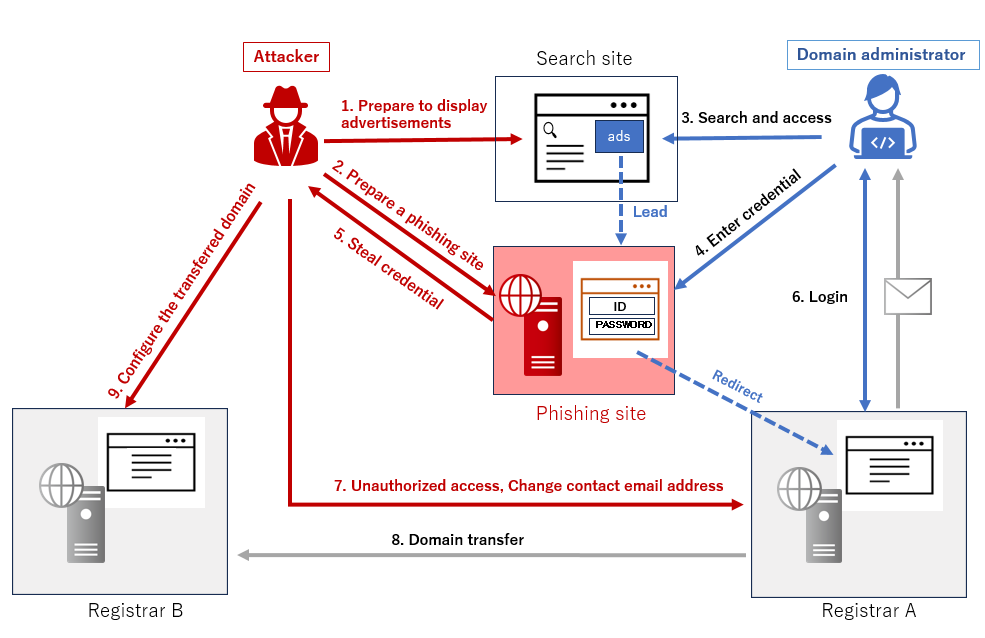
Attackers pilfer tokens, passwords, keys, or usernames to impersonate users or heighten privileges. Credential theft is accelerating, with a 42% year-over-year surge in most accounts.
AI & Deepfake Attacks
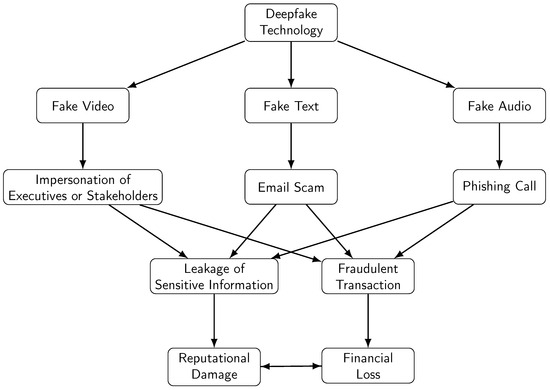
New threats where cybercrooks leverage AI to generate advanced impersonations, phishing emails, or craft malware. Social engineering attacks are more labor-intensive with the aid of generative AI.
In 2024–2025, 79% of the detections were clean malware, i.e., new-generation threats do not rely on conventional malware signatures and employ more stealthy tactics, according to Crowdstrike.
New Cyber-Security Threats & Trends
Cyber-security is never at rest. Some of today’s most threatening dangers are:
- AI-Based Cyber Attacks: Phishing and malware become sophisticated with hackers using artificial intelligence.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Low-capacity assailants are able to lease ransomware tools.
- Remote Work Risks: Home networks and personal computers left unprotected exhibit weakness.
- Cloud Security Threats: Cloud storage mistakes tend to leave sensitive data open to attack.
- Cyber Espionage: Governments and organizations employ hackers for political or military gain.
Cyber-Security Best Practices: How to Stay Safe
Protecting yourself online isn’t always about having high-tech gear good habits do the trick:
- Software Updates: Install operating system/apps updates and security patches.
- Good Passwords & MFA: Do not use weak or duplicate passwords, and turn on two-factor authentication.
- Be cautious of Suspicious Links: Do not open new links from emails or messages.
- Secure WiFi Networks: Turn on WPA3 encryption and only use public WiFi rarely for urgent work.
- Regular Back Up Data: Maintain offline or cloud backups for ransomware restore.
- Installation of Trusted Antivirus & Firewalls: Guard against malware.
- Training in Cyber Hygiene: Guard against scams, phishing, and spoofed websites.
Final Thoughts
Cyber-security is no longer a choice, but now an imperative for governments, all commerce, and citizens alike. As ever more sophisticated cyber threats are evolving, education, policy, and technology are the sole recourse. From guarding one’s mail to safeguarding national defense systems, investment in cyber-security today prevents catastrophes tomorrow.
To explore more insights like this, visit our Cyber-security Page.
If you’re passionate about tech, networks, and digital infrastructure, Write for Us and share your voice with our audience.