Cyber-attacks are rising rapidly in today’s digital-first era. From Phishing to ransomware, new methods of victimizing susceptible systems are being released by cybercriminals on a daily basis. One of their top targets? Endpoints-the laptops, desktops, servers, and mobile devices users are accessing daily to link to corporate networks.
This is where endpoint security steps in. Securing these entry points, endpoint security is the initial line of defense and final line of defense against cyber threats. For individuals, governments, and organizations, endpoint security is no longer a choice, it’s a requirement.
In this blog, we’ll explore what endpoint security is, why it’s important, how it works, its core components, benefits, and future trends. By the end, you’ll know exactly why investing in strong endpoint protection is critical for survival in today’s digital age.
What is Endpoint Security?
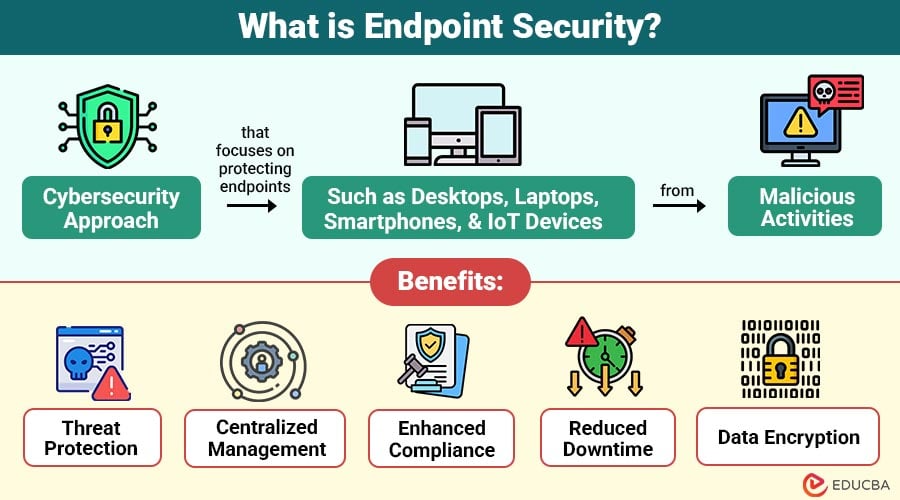
Endpoint security is the practice of safeguarding all end-user devices such as laptops, desktops, smartphones, servers, and Internet of Things devices that connect to a corporate network against malicious cyber behavior.
The endpoints, or in this case, the devices, are virtual entry doors to a firm’s sensitive information and IT system. Exposed, they can be susceptible to being accessed by hackers as a point for malware, ransomware, or data exfiltration.
Picture endpoint security as having a guard at each door of a building. Regardless of how the attackers attempt to enter through the tiniest or most improbable door, there’s some kind of defense.
Examples of Endpoints: laptop, desktop, server, mobile device, IoT devices, and printers.
Why is Endpoint Security Important?
Endpoint security cannot be overemphasized. Here’s the reason why endpoint security is a top priority for businesses and users nowadays:
1. Endpoints are vulnerable targets
Endpoints are being exploited as they are most likely to be the weakest point in the network. One infected laptop can infect the whole company.
2. Issues related to BYOD and remote work
With employees remotely located and under “Bring Your Own Device” (BYOD) initiatives, workers access business networks on their own devices. Those devices are not necessarily as secure, exposing vulnerabilities.
3. Data protection and compliance
Sensitive information like financial information, customer data, and intellectual property typically sit on endpoints. Protecting that information is necessary in an effort to remain compliant with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
4. Increased cyberattacks
Ransomware, phishing, and sophisticated malware attacks are becoming more common by the minute. They typically begin as a single vulnerable endpoint.
5. Business continuity and reputation
A successful attack can cost money, lead to lawsuits, time spent in downtime, and reputational loss. Endpoint security avoids all these threats.
In short, without strong endpoint security, every device in your network is an open window for attackers.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
Endpoint security works through a blend of policies, monitoring applications, and software that all work together to secure devices and networks. Here’s how it works:
1. Centralized Management Console
IT administrators manage endpoint security from one point of management. In this manner, all devices that are connected use the same security policy.
2. Endpoint Agents or Client Software
Security agents are installed on every endpoint. They scan the device automatically for malicious activity or malware.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
The system monitors endpoints for suspicious activity, such as unwanted access or suspicious file activity, and alerts administrators.
4. Threat Detection and Response
Endpoint security not only identifies threats but even quarantines or blocks the malware files. The next-generation ones such as EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) and XDR (Extended Detection and Response) go a step further and carry out threat pattern analysis.
5. Cloud and AI Integration
Solutions now employ AI and machine learning to find threats quicker, and sometimes identify new malware even before it’s very prevalent. Cloud-based infrastructure enables real-time pushing of updates, cutting down on vulnerabilities.
Basically, endpoint security is a 24/7 sentinel that finds, stops, and removes threats before anything is affected.
Quick Link: What is 5G Network Security? A Complete Guide
Key Elements of Endpoint Security Solutions
A decent endpoint security solution has several layers of protection. These are the key elements:
- Antivirus & Anti-malware: Removes viruses, trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
- Firewalls: Blocks incoming and outgoing traffic and blocks unauthorized access.
- Encryption & Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Ensures sensitive information is kept safe by encrypting files and preventing unauthorized transfer or sharing.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR/XDR): Ensures advanced threat detection, incident response, and forensic analysis.
- Application & Device Control: Prevents unauthorized applications, USBs, or peripherals from being used.
- Patch Management: Keeps endpoints updated with security patches to seal known weaknesses.
- Behavioral Analysis: Identifies suspicious behavior through examination of patterns e.g., speedy file encryption (a ransomware warning sign).
- Zero-Trust Security: Requires ongoing device and user authentication with no endpoint ever trusted.
All of these elements combined are a stacked defense model, so even if one security process is compromised, others still safeguard the device.
Advantages of Endpoint Security
Efficient endpoint security provides some benefits to businesses and individuals:
- Protects sensitive information from leaks and breaches.
- Protects remote employees through policies and monitoring.
- Limits ransomware attacks and malware infection.
- Reduces industry regulation compliance risk.
- Reduces downtime through system disruption prevention.
- Builds customer trust through display of proper cybersecurity.
If endpoint security is not utilized, businesses risk unnecessary threats that amount to millions in loss.
Endpoint Security vs Antivirus
Endpoint security tends to be confused with traditional antivirus software by others. Although both of them guard against threats, they are not the same.
- Scope: Antivirus guards an individual device; endpoint security guards all devices that are inter-connected.
- Threat Coverage: Antivirus guards against known malware only; endpoint security guards against sophisticated attacks such as ransomware and phishing.
- Updates: Antivirus needs to be updated every so often manually; endpoint security leverages cloud smarts to be constantly protected.
- Control: Antivirus is managed by the end-user; endpoint security is IT centrally managed.
- Level of Protection: Antivirus is partial; endpoint security is total.
In all but the most technical senses, antivirus is actually a type of endpoint security.
Endpoint Security vs Firewall
One other fuzzy misunderstanding is between firewalls and endpoint security.
- Firewall: Manages network traffic by blocking unauthorized connections.
- Endpoint Security: Safeguards the device itself, i.e., user activity, applications, and files.
- Together: They are complementary. Firewalls keep outside intrusions at bay, and endpoint security keeps in-house action safe.
Best Practices for Successful Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is not a matter of software installation alone, success is a matter of strategy. Try out these best practices:
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Update and patch all devices regularly.
- Implement a zero-trust policy on users and devices.
- Ongoing security education of employees.
- Facilitate data backup and recovery capabilities.
- Endpoints constantly monitored for anomalies.
- Privilege and access limitation of users.
All these measures actually lower the likelihood of a successful attack.
The Future of Endpoint Security
Cyberattacks, much like technology itself, are changing. The future of endpoint security will be all about:
- AI-driven detection: Intelligent, autonomous response to threats.
- Zero Trust growth: Validating every device and connection.
- Cloud-native protection: Flexible, scalable defense.
- IoT and edge security: Protecting billions of smart devices.
- Predictive analytics: Preventing attacks from occurring.
Endpoint security is no longer all about reacting to attacks when they occur. It’s moving toward proactive prevention.
Conclusion
Today’s interconnected world means that every device is a potential entry point for cyber attackers. Endpoint security protects these devices with layer upon layer of defense, anything from antivirus to encryption, firewalls to advanced EDR solutions.
With robust endpoint protection in place, businesses can safeguard important data, achieve compliance, and remain resilient against ever-evolving cyber threats.
The reality is simple: if you’re not securing your endpoints, you’re leaving your entire network exposed.
To explore more insights like this, visit our Cyber-security Page.
If you’re passionate about tech, networks, and digital infrastructure, Write for Us and share your voice with our audience.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of endpoint security?
The primary function of endpoint security is to protect laptops, desktops, and mobile phones from cyber threats, keeping data and business systems secure.
Is endpoint security the same as antivirus?
No, Antivirus just guards known malware on one device, whereas endpoint security gives protection to the entire group of devices that are connected in a network.
Why do companies require endpoint security?
Endpoint security protect sensitive information, mitigates compliance risk, halts downtime, and fosters business continuity against increasing cyberattacks.