With the highly networked world that we have today, the threats in the virtual world are increasing by size and kind. You may be an individual user of the internet or a multinational company with a thousand applications to sort out, but your online life is always at risk. From nefarious hackers attempting to steal important data to viruses in regular downloads, dangers can approach from all sides. Firewalls, the quiet protectors that determine what comes in and goes out of your virtual world, save the day.

A firewall is more than just a technical tool; it is the backbone of modern cybersecurity. In this blog, we’ll break down what a firewall is, how it works, why it’s important, best practices for management, common mistakes to avoid, and what the future of firewalls looks like.
What is a Firewall?
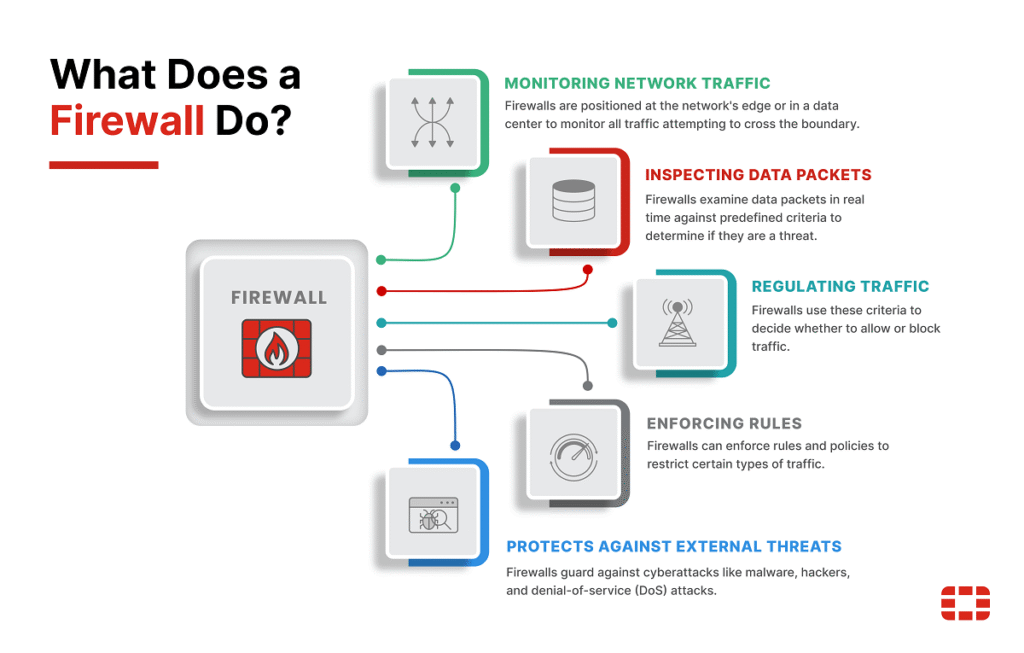
A firewall is essentially a safety device that examines and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic against a previously defined set of security rules. It’s similar to a safety barricade: all the data (a packet) which is attempting to get into or out of your network must pass through the firewall, and it will decide whether or not to let it in or out.
The main job of a firewall is to make a border between an internal trusted network (like your wireless or business network at home) and an external untrusted network (like the internet). This way, firewalls block unwanted access, block malicious traffic, and reduce the possibility of cyber-attacks.
Firewalls have evolved. What were once packet filters are today next-gen, AI-powered, and cloud-native firewalls that support very adaptive and advanced threats.
How Do Firewalls Work?
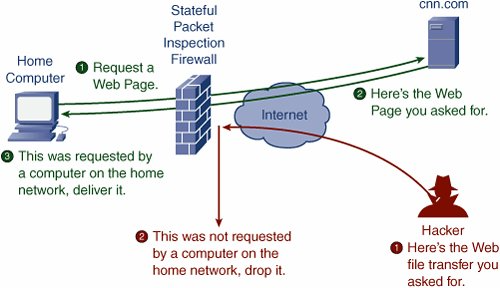
Firewalls operate on predefined policies and rules, which determine the kind of traffic that can pass. When data packets move through a network, each packet contains header information such as source, destination, port, and protocol. The firewall examines this information and makes a decision:
- Allow the packet if it adheres to known security rules.
- Block the packet if it discloses patterns of malicious or unauthorized activity.
Key Methods Used by Firewalls:
- Packet Filtering: Inspecting packet headers and allowing/denying according to IP address, port, and protocol.
- Stateful Inspection: Monitoring the status of ongoing connections to verify if a packet is part of an established, legitimate communication.
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Inspecting within the packet payload to locate malicious code, viruses, or prohibited content.
For example: Let’s say you try to go to a website. When your computer requests it, the firewall checks it against its rules. If the site is secure, it’s passed through. If it’s malicious (a phishing site, for example), the firewall blocks it from hitting you.
It happens in the flash of an eye, so firewalls are quick and effective.
Why Are Firewalls Important?
Firewalls are commonly referred to as the frontline of cyber security and rightly so. Without firewalls, networks would be fully vulnerable to cyber attacks. The following are the main reasons why firewalls cannot be omitted:
1. Protection against Cyber Attacks
Firewalls prevent unauthorized users, malware, ransomware, Phishing, and other harmful traffic from accessing your system.
2. Protection of Sensitive Data
Organizations contain sensitive information such as customer information, financial data, and intellectual property. A firewall prevents the data from leaking or being hacked.
3. Regularity Compliance
Some businesses (finance, health, commerce) are under a legal obligation to protect customer information. Firewalls aid in compliance with legislations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
4. Maintaining Network Integrity
Firewalls permit acceptable traffic through unaffected while blocking malicious interferences like Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks.
5. Digital Trust Establishment
Business partners and customers also anticipate being in a secure digital environment. Safety comes with a good firewall, which creates trust and credibility.
Benefits of Firewall Use
Firewall use is more than “prevent bad traffic.” Some of the most significant benefits are:
- Network Security: It blocks intrusions and unauthorized accesses.
- Visibility & Control of Traffic: Admins get to know what is happening within the network and can implement rules for allowed traffic.
- Reduced Data Breach Risks: Protects against financial loss and reputational damage.
- Multi-Layered Security: Augments antivirus, intrusion detection (IDS), and endpoint security to offer a robust defense model.
- Sense of Security: People and businesses can do it online with peace of mind with threats filtered and tracked.
Selecting the Right Firewall
Since you already have a specialized in-depth post on firewalls types, here we won’t discuss details on them. Let’s discuss what to look for while choosing a firewall solution.
- Security Requirements: Small businesses would do with a basic firewall, while large companies require next-generation firewalls with intrusion prevention, application control, and artificial intelligence-based threat detection.
- Performance: The firewall should handle your network bandwidth without negatively impacting performance.
- Scalability: As your company grows, the firewall must be able to support greater traffic and infrastructure.
- Management & Simplicity: Easy-to-use consoles, central management, and cloud management make administration easier.
- Budget: Functionality vs. cost. Paying through the nose for unused functionality is as useful as failing to adequately protect valuable information.
Related: Types of Firewalls to Secure Your Network
Best Practices for Firewall Management
Even the most powerful firewall won’t save you if it is not managed correctly. These are practices that all organizations (and people) should embrace:
- Update Firewall Rules Regularly: Periodically assess and refine rules to cover emerging threats and changing business environments.
- Patches and Updates Regularly: Outdated firewalls are an open invitation for the bad guys. Apply the latest security patches at all times.
- Continuous Monitoring: Look out for suspicious behavior and anomalies from traffic logs.
- Avoid Over-Complication: Copycat policies everywhere create blind spots. Keep it simple and organized.
- Security Audits on a Regular Basis: Test the firewalls and identify holes through frequent audits.
- Segmentation: Network segmentation through firewalls to reduce the probability of a single point of entry leading to a breach of the entire system.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even though firewalls work, they are not properly configured in most organizations. Avoid the following most common errors:
- Reliance on Default Settings: Default settings are not tailored to your environment and have holes in them.
- Ignoring Updates: Unpatched and outdated firewalls are an attack in the making.
- Not Monitoring Logs: Logs contain valuable information regarding attempted intrusions, not reading them is equivalent to disregarding warning signs.
- Overlooking Cloud Compatibility: There are some contexts of modern-day IT deployments where firewalls need to be cloud-compliant with hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
- Assuming Firewalls Are Enough: Firewalls are important, but they need to be paired with a wider cybersecurity strategy.
The Future of Firewalls
Cyber threats also constantly evolve, and firewalls also keep on evolving. The future is more intelligent, quicker, and adaptive firewalls.
1. Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
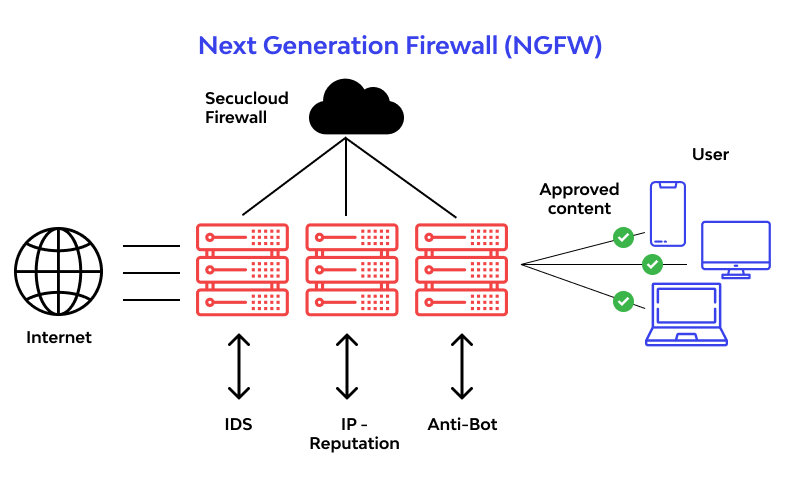
NGFWs are more than just filtering. They are equipped with application awareness, intrusion prevention, and built-in threat intelligence.
2. AI and Machine Learning
AI-based firewalls can analyze network flows in real-time, detect unknown threats, and dynamically change security policies autonomously.
3. Cloud and Hybrid Security
With cloud workloads shifted to cloud environments, cloud-native firewalls provide flexible and scalable security without impairing performance.
4. Zero Trust Integration
Upcoming firewalls will include native Zero Trust architectures that validate all requests regardless of their source.
In short, firewalls are no longer static blockers now, they will be evolving to become intelligent security platforms that can learn how to adapt to the evolving cyber environment.
Quick Link: What is Endpoint Security? Definition, Importance & How It Works
Final Thoughts
Firewalls remain near the top of the list of best cybersecurity solutions available today. They shield solo operations from nasty websites, and they shield sophisticated enterprise networks. Firewalls are the protectors of web security.
By understanding what a firewall is, how it works, and why we have it, organizations and individuals can proactively move in the direction of enhanced security. By following best practices, not committing common mistakes, and preparing for the future of smart firewalls, you are ahead of time in managing evolving cyber threats.
Today, in a technological age, firewall protection is not an option, it is essential.
To explore more insights like this, visit our Cyber-security Page.
If you’re passionate about tech, networks, and digital infrastructure, Write for Us and share your voice with our audience.
FAQs
What is the main role of a firewall?
The primary role of a firewall is to protect networks and devices against unauthorized access and damage traffic by analyzing packets of data based on security policies.
Do home users need a firewall?
Yes, although most users rely on the built-in firewall of the router, having a separate firewall installed or activating firewall software on devices is an additional layer of protection against malware and hackers.
Will a firewall stop all cyberattacks?
There is no single tool that will stop all cyberattacks. Firewalls are great, and they need to be used in combination with antivirus, intrusion detection, and regular security to be completely safe.