In the era of fast-evolving technological advancements, the healthcare sector has undergone an unprecedented transformation. This shift from conventional systems to digital systems results in enhanced patient care services, efficient record-keeping, and innovative telemedicine practices. Now we are living in a world where patient data is just a click away, where doctors can be approached across borders, and not only this, the medical devices are interconnected for real-time monitoring. This sounds good but this advancement has also raised many questions regarding cybersecurity in healthcare.
In this article, we will highlight the need and importance of cybersecurity in healthcare, So stay connected.
Cybersecurity in Healthcare:
Cybersecurity in healthcare is a set of practices and protocols designed and implemented to protect sensitive patient data and medical records. The aim is to protect organizations from both internal and external cyberattacks, ensure the availability of medical services, ensure the proper operation of medical systems and equipment, preserve patient confidentiality, and comply with industry regulations by taking a variety of measures. Moreover, cybersecurity in healthcare acts as a protective shield against the growing threats that healthcare organizations are facing in this Computer age.
In 2021, the global healthcare cybersecurity market was valued at 14.79 billion U.S. dollars. Moreover, the market is expected to grow significantly over the years. By 2030, the cybersecurity market is thought to surpass 58 billion U.S. dollars worldwide.
Source: Statista
Why do hackers target healthcare?
The Healthcare Industry extending from Hospitals, Pharmacies, Community Care centers, and Clinical Trials agencies to Pharmaceutical Industries has historically been a primary target of cyberattacks. These cyberattacks can range from data breaches and ransomware attacks to compromised medical devices. Among the reasons for this are: Healthcare organizations handle huge amounts of personal and private information, which is extremely valuable to criminals. According to Beckers Health IT, more than 90% of hackers have a financial motive.
Why Cybersecurity in Healthcare is important?
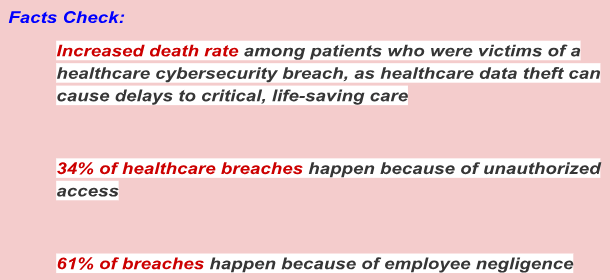
Over the past few years, an increasing trend in cyber attacks is observed globally, and among this healthcare industry is ranked on top. Statistics showed a continuous rise in the healthcare data breach between 2020 and 2021 that was an all-time high i.e. 663 in 2020 to 679 in 2021.
As discussed earlier that the healthcare industry is the favorite target of cyberattackers, Cybersecurity in healthcare plays a decisive role in protecting the healthcare industry against a number of potential threats: Let’s explore some of these threats:
- Patient Data Breaches and Privacy Violations:
Patient data is considered a treasure trove for cyber attacks. All Patient data including Personal Information, Present and past medical histories, and financial records can be sold on the dark web with the intention of theft and fraud.
According to the report by Fierce Healthcare, the black-market value of medical records is at least $250 and as much as $1000 Credit card numbers, on the other hand, sell for around $5 each, and Social Security numbers can be purchased for as little as $1 each.
How to Control:
The best way to control this is the utilization of cybersecurity in healthcare tools that include data encryption and access controls for preventing unauthorized data breaches.
- Ransomware Attacks:
Due to the high prevalence of ransomware, cybersecurity in healthcare is crucial. It is designed to deny a user or organization access to files on their computer. By encrypting these files cybercriminals demand ransom payments for its release. Ransomware is the most disruptive type of attack that leads to the most operational delays.
The largest ransomware attack on a hospital in 2022 was the Chicago-based CommonSpirit ransomware attack that compromised the data of 623,000 patients. Source: Beckers Health IT.
How to Control:
In order to prevent such attacks and ensure that patient care is not compromised, robust cybersecurity protocols are necessary in the healthcare sector.
- Medical Device Vulnerabilities:
There are a number of cybersecurity challenges associated with the increasing use of connected medical devices. Hackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in devices like insulin pumps or pacemakers, endangering patient safety.
Up to 50% of all Internet of Things (IoT) devices in hospitals are vulnerable to attacks.
How to Control:
Cybersecurity practices must be extended to these devices to mitigate potential risks.
Takeaway:
The need for cybersecurity in healthcare is not a passing trend but an ongoing commitment. For healthcare organizations to stay one step ahead of potential threats, they must stay vigilant, continually updating and upgrading their cybersecurity measures.
In the end, the digital transformation of healthcare is a remarkable journey that promises better patient outcomes and enhanced medical services. However, this journey must be undertaken with a strong focus on cybersecurity in healthcare.
FAQs
What is health cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity in healthcare is a set of measures aimed at protecting patient profiles, medical records, and healthcare systems from cyber attackers. It includes the protocols to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, all while preventing cyberattacks.
What is the use of cybersecurity in healthcare?
The purpose of cybersecurity in healthcare is to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks that could compromise patient privacy, disrupt medical services, or even put patients’ lives at risk.
What is the importance of cybersecurity in the healthcare industry?
In the healthcare industry, cybersecurity is extremely important because patient data is sensitive and cyber threats can pose significant risks. In addition to preventing data breaches, it protects patient safety by ensuring the integrity of medical devices and systems, and it ensures regulatory compliance to avoid legal and financial penalties.