Scanning technology also turns the pages with the moving world. QR codes are the modern form of barcodes, which are used to track products in retail settings. Barcodes set limits when it comes to data storage and capacity, and here Japanese company Denso Wave launched QR codes. But what does QR stand for? Question alert!
Read the article and get your answer to all questions regarding QR codes.
What Does QR Stand For, and What Is QR Code?
QR stands for “Quick Response.”
QR codes are barcodes that store and transmit data in a grid of black-and-white squares, or pixels. It contains information or data about products in a supply chain and facilitates payments. Smartphone cameras have a built-in QR code reader that decodes the information in human language in seconds.
How Do QR Codes Work?
QR codes seem more versatile than traditional barcodes, as they store information both horizontally and vertically. This allows them to hold more than 100 times the data. You can use QR codes to encode a wide range of information, which includes:
- Website URLs
- Email addresses
- Wi-Fi network details
- Menu items
- Product information
Common Uses of QR Codes
Here, we have uses of QR codes.
- Marketing and Advertising: Users can access websites or promotions by scanning codes on posters or packaging.
- Payments: QR codes are used by many digital payment systems to facilitate safe and speedy transactions.
- Access Control: The use of QR codes for contactless check-ins, including event admission or hotel room access, is growing.
How do I scan QR codes?
You can scan a QR code using either your device’s camera or a QR reader app.
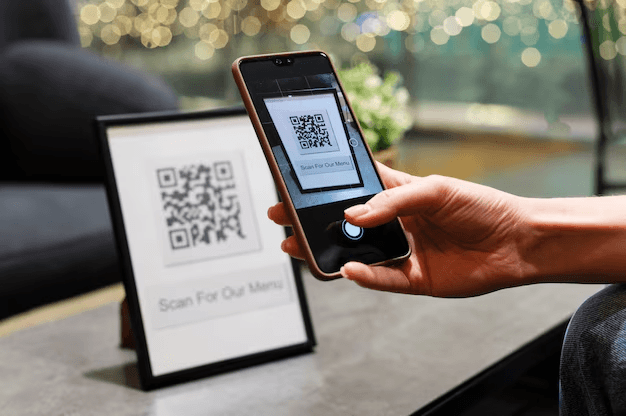

- Steps to scan the QR code if you have Android:
- Open the camera app
- Point it at the QR code,
- Tap the banner that appears.
- You can also use Google Lens, which is integrated into some apps like Google Camera, Chrome, and Photos.
- To use Google Lens,
- Open the app
- Point it at the QR code for a few seconds
- For iPhone, iPad, or iPod touch, you can use the built-in camera to scan the QR code.
Common QR Code Cybersecurity threats
Cybersecurity threats are everywhere. How is it possible that QR code scanning remains free?
Let’s learn the threats that can be harmful.
- Phishing attacks: QR codes redirect users to phony websites and fool them into providing sensitive information.
- Malware Installation: Scanning a QR code may result in the automatic installation of harmful apps or files, particularly on devices with security flaws.
- Payment Fraud: When processing digital payments, hackers may substitute authentic codes with phony ones, causing money to be sent to their accounts.
How to Use QR Codes Safely

Check out the safety tips for using QR codes.
1. Verify the Source
Always keep yourself alert before scanning the QR code. Examine the source and determine whether it is from a familiar and trustworthy source. Double-check if you receive one from an unexpected sender via email or social media.
2. Preview URLs When Possible
Some QR scanning programs and smartphone cameras provide a preview of the URL before scanning it. Use this feature to check the URL for any strange or suspicious domains. Further, if you scan it, avoid entering any personal information on a web page or app, as it could be a phishing scam.
3. Avoid Scanning Random Codes in Public
Hackers may plant dangerous QR codes in public places. Stick to the codes on reputable websites, official papers, or well-known companies. Also, keep your eyes sharp when scanning in public; look for your surroundings.
4. Install Security Software
Install a mobile security app that includes QR code scanning and built-in security measures, particularly for Android devices. Antivirus software will safeguard your device from viruses and other malware assaults when scanning QR codes.
5. Disable Automatic Actions
Make sure that your device does not perform any automatic actions after scanning a QR code, such as downloading programs or opening websites without authorization. This can make any virus enter your device.
Final Thoughts: Staying Secure in a QR-Driven World
QR codes are the most adapted scanning technology used by local vendors, business owners, and marketing firms. When you decode the phrase “What does QR stand for?” the term quick response makes you believe in accessing information in one go. The convenience we enjoy also brings threatening security risks, but handling and understanding the technology gracefully can become a win-win situation for you.
Don’t just scan away; be alert and stay safe!
Explore recent cybersecurity news and guides if you missed any.
If you’re interested in contributing, submit your guest post and Write for Us.